
Experiencing a sudden black screen and PC shutdown while gaming? It’s likely your GPU is overheating. But don’t worry! GPU overheating is common and easily fixable. In this guide, we’ll explore what happens when GPU overheats, how to recognize it, and most importantly, how to prevent it from happening again. We’ll cover optimal GPU temperatures, troubleshooting, easy hardware maintenance, software programs for upgrades, and when it’s time to upgrade your card. With the right advice, you will soon be able to get back to gaming and upgrading your GPU. Let’s get involved!
Signs Your GPU Is Overheating
Uh-oh, is your graphics card running hot? Overheating can cause serious damage to your GPU, so it’s important to recognize the symptoms early on. Here are some signs that your GPU may be overheating:
1. Loud Fan Noise
Your GPU has a built-in fan to keep the heat on. If the fan has been running at full speed for a long time, it probably means your GPU is overheating. You may hear loud roaring or humming sounds coming from the computer. This fan works overtime to cool an overheated graphics card.
2. Screen Artifacts
When a GPU overheats, it can start to glitch and display visual artifacts on screen. You may notice strange pixelation, distortion, or colorful dots/squares on your display. These artifacts indicate your graphics card is struggling at high temperatures.
3. Game Crashes
If your GPU gets too hot during gameplay, it may cause games to crash unexpectedly. Overheating GPUs have trouble rendering graphics and can freeze or shut down games to prevent permanent damage. Repeated game crashes are a sign your graphics card needs better cooling.
4. Blue Screen Errors
Overheating and other GPU and hardware issues are often the cause of the dreaded “blue screen of death”. Blue screen errors, also known as BSODs, indicate that your graphics card has reached critical temperature and you should shut it down immediately to avoid irreparable damage If you see a blue screen error related to your graphics card or video driver a, the excessive heat may be to put on.
Also Read: Is 80 Degrees Celsius Hot for a GPU? Find Out Here!
Causes of GPU Overheating
1. Lack of cooling
The most common cause of GPU overheating is simply inadequate cooling. Your graphics card produces a lot of heat when it’s working hard, like when you’re gaming or doing GPU-intensive tasks. If that heat isn’t dissipated efficiently, temperatures will rise until the GPU starts throttling or shuts down completely to avoid permanent damage.
2. Dust buildup
Over time, dust can collect on computer components like the graphics card heatsink and fans. This dust acts as an insulator, trapping heat in and reducing the efficiency of the cooling system. It’s a good idea to physically inspect your GPU fans and heatsinks regularly and blow out any built-up dust with compressed air. Be very careful not to spin the fans too quickly, as this could potentially damage them.
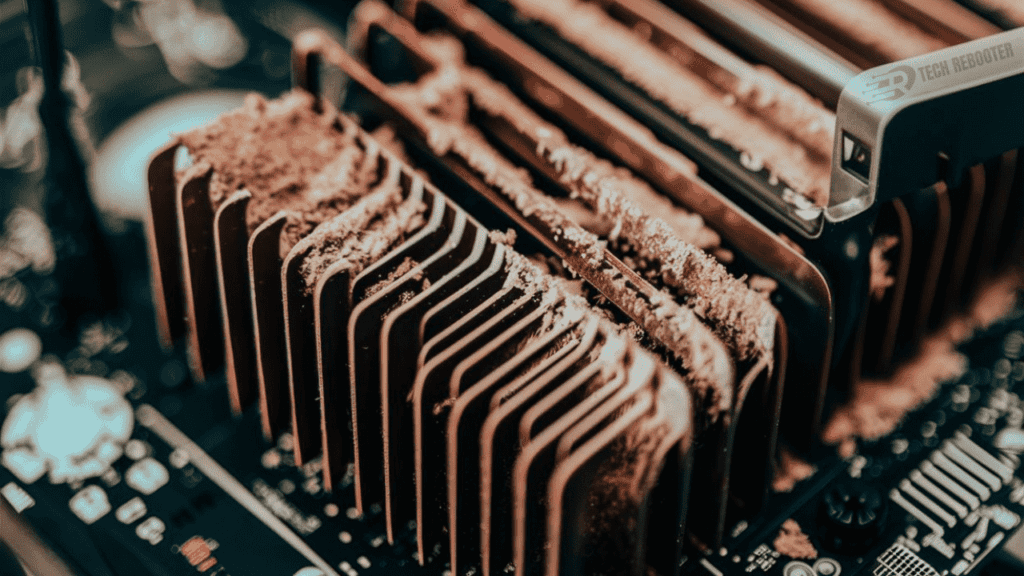
3. High workload
Pushing your graphics card too hard for long periods of time can also contribute to overheating. When your GPU has to work at maximum capacity for long periods of time, such as during an intense gaming session, heat can build up faster than the cooling system can dissipate. If you experience GPU overheating during demanding tasks, you may want to improve your cooling setup or consider a more powerful graphics card.
4. Software issues
Sometimes software glitches or bugs can cause GPU overheating. Outdated or missing graphics card drivers are a common culprit. Make sure you have the latest drivers for your GPU installed. You may also want to disable any overclocking software when troubleshooting overheating, as this can stress the graphics card. If problems persist, you may need to update other system drivers or firmware, reinstall the GPU drivers, or reset your BIOS to default settings.
Consequences of Overheating GPUs
Your graphics card is the heart of your PC’s gaming performance, so overheating it can cause serious harm. An overheated GPU can experience permanent damage, drastically impacting how well it works. Pay attention to the signs before it’s too late.
1. Performance Drops and Visual Artifacts
As your GPU temperature increases, you will see latency, stuttering, and frame rate decrease during games. To avoid overheating, the graphics card needs to restrict performance, but even that may not be enough. Visual artifacts, like screen tearing, may also appear. These issues will continue to worsen until the temperature is reduced.
2. System Crashes and Shutoffs
If your GPU gets too hot, your entire system may crash or abruptly shut off as a failsafe to avoid damage. This is a critical warning that your graphics card needs immediate cooling. Continuing to run intensive tasks can potentially lead to permanent damage.
3. Long-Term Damage
Prolonged overheating can physically damage your GPU over time through a process called electromigration. Parts of the integrated circuits start to degrade and break down. You may experience permanent performance issues, system instability, or even complete GPU failure. Replacement or repair of the graphics card will likely be required.
The best way to avoid all these problems is through prevention – regularly monitor your GPU temperature, provide adequate cooling, and avoid overloading your graphics card whenever possible.
How to Cool Down an Overheated GPU
Overheating is a major problem for graphics cards and can severely impact their performance and lifespan. If your GPU is running hot, it’s important to take action quickly to prevent permanent damage. Here are some steps you can take to chill out your overworked graphics card.
1. Improve Airflow
The easiest way to lower your GPU temperature is by improving airflow around the card. Make sure your computer case has good ventilation and any installed case fans are clear of dust and debris. You may need to adjust or replace existing fans to increase airflow. Also, ensure there is adequate space around and behind your computer tower so heat can properly dissipate. Improving airflow is an easy fix and should be your first step.
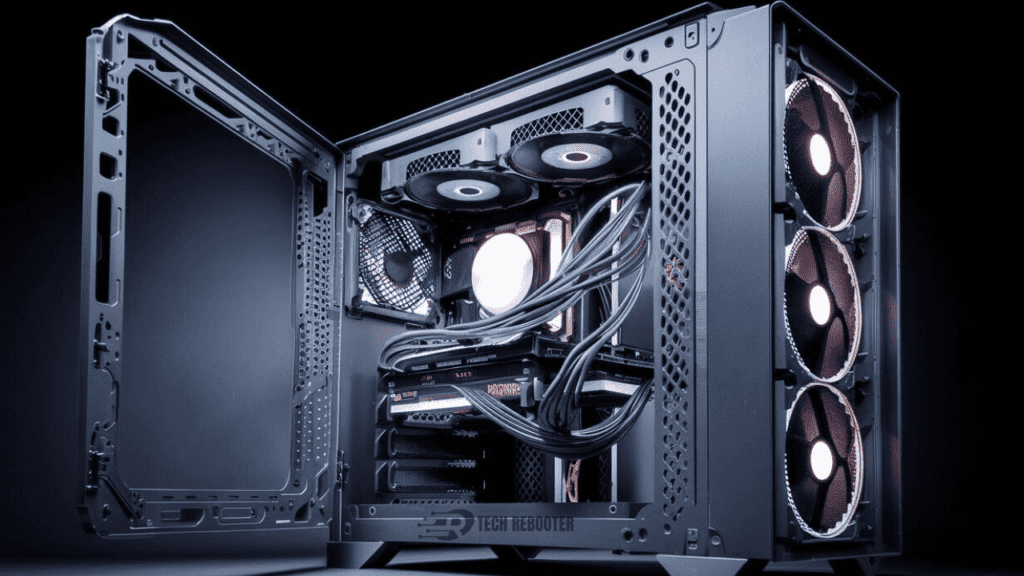
2. Underclock Your GPU
If your graphics card is overclocked, it’s running at a higher frequency than intended which generates extra heat. Underclocking your GPU reduces its clock speed and voltage, thereby lowering the temperature. You can underclock using the graphics control panel software for your specific graphics card. Lower the core clock speed and memory clock speed in small increments until you achieve a stable, lower temperature. Underclocking may reduce performance slightly but is better than an overheated GPU.
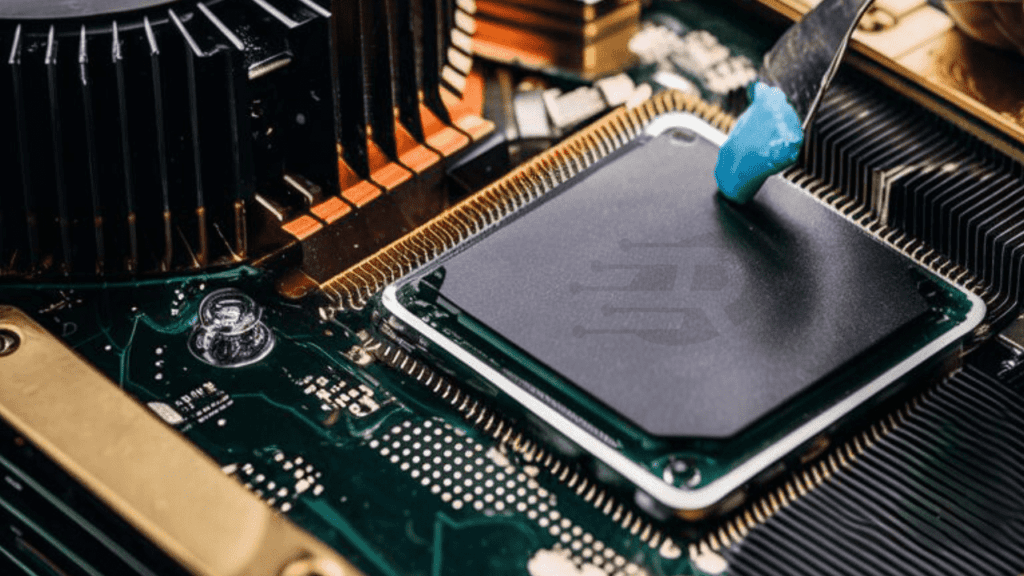
3. Repaste Your GPU
The thermal paste between your graphics card’s GPU chip and the heatsink can dry out or become ineffective over time, reducing heat transfer. Cooling can be greatly improved by removing your GPU coolant, cleaning out old thermal paste, and replacing it with high-quality paste. However, repasting is an advanced process and can be difficult, so only attempt this if you have experience building and repairing PCs. It also may void your warranty, so check first.
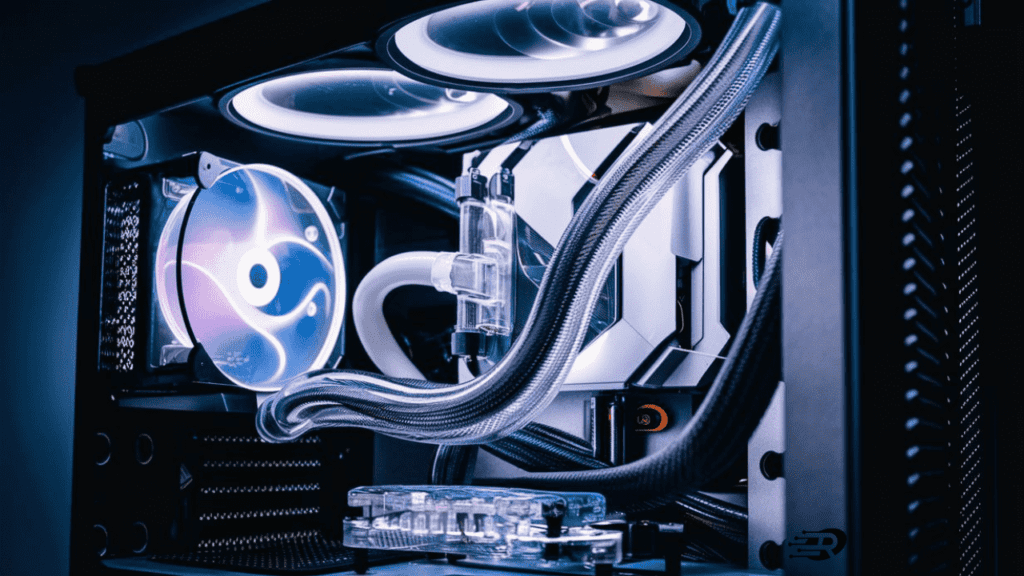
4. Liquid Cooling
For persistent overheating problems or overclocked high-end GPUs, a liquid cooling system may be necessary. Liquid cooling, such as an all-in-one CPU cooler or custom water loop, is very effective at drawing heat away from components and keeping temperatures in check. However, liquid cooling systems tend to be expensive and difficult to install, requiring modification of your computer case and other components. Liquid cooling should only be considered for serious cooling needs or by experienced PC builders.
By making a few adjustments to improve airflow, underclocking your GPU, repasting the cooler, or considering an advanced liquid cooling setup, you can get your graphics card temperature under control and avoid the damaging effects of overheating. Keep a close eye on your GPU temperature and take action quickly if it starts running hot again.
FAQs
What are the signs of GPU Overheating?
- Symptoms of a GPU overheating include sudden shutdowns, screen flickering, artifacting (displaying unusual graphical glitches), and performance drops in graphics-intensive tasks or games.
What happens when GPU overheats?
- When a GPU overheats, it can lead to reduced performance, system instability, and potential permanent damage to the graphics card. To prevent overheating, ensure proper airflow, clean the cooling system regularly, and consider additional cooling solutions.
How does overheating affect GPU performance?
- Overheating can lead to reduced performance as the GPU attempts to throttle itself to lower temperatures, resulting in slower frame rates, stuttering, and decreased overall system responsiveness.
Can overheating damage a GPU?
- Yes, prolonged overheating can cause permanent damage to the GPU, potentially leading to hardware failure, graphical artifacts, and in extreme cases, rendering the GPU unusable.
How to fix an overheating GPU?
The best way to deal with an overheated graphics card is to improve cooling. Below are a few actions you can take::
- Clean your PC case and graphics card fans to remove dust buildup.
- Increase case fan speeds or add additional case fans to improve airflow.
- Replace the thermal paste between the GPU die and heatsink.
- Underclock your graphics card to run it at lower power and temperature levels.
- You may need to replace a faulty graphics card fan or heatsink to restore proper cooling.
How do I check GPU temperatures?
- You can monitor GPU temperatures using software utilities such as MSI Afterburner, GPU-Z, or the built-in monitoring tools provided by your GPU manufacturer’s software suite.
What should I do if my GPU overheats?
- If your GPU overheats, immediately stop any intensive tasks or gaming sessions, shut down your system, and allow the GPU to cool down. Consider improving your system’s cooling capabilities or consulting a professional if overheating persists.
Can overclocking cause GPU overheating?
- Yes, overclocking can increase the heat output of the GPU, leading to higher temperatures and an increased risk of overheating. Proper cooling solutions and monitoring are essential when overclocking to prevent damage to the GPU.
How often should I clean my GPU to avoid overheating?
- It’s recommended to clean your GPU and the surrounding components every few months, or more frequently if you notice increased temperatures or performance issues. Regular maintenance helps prevent dust buildup and ensures optimal cooling efficiency.
Can GPU overheating impact system stability?
- Yes, GPU overheating can affect system stability by causing crashes, freezes, or instability during operation. Maintaining proper temperatures is crucial for ensuring reliable performance and prolonging the lifespan of your GPU.
Conclusion
So there you have it – the lowdown on what happens when your GPU overheats. From slight performance drops to full system crashes, it’s something every gamer wants to avoid. Keeping your GPU properly cooled with quality fans and thermal paste is key, along with cleaning out dust buildup regularly. And if you start noticing artifacts, crashes, or abnormal temps, it’s time to take action. Hopefully now you’re armed with the knowledge needed to keep your card cruising along at safe operating temps for many hours of smooth gaming ahead. Just remember – a cool GPU is a happy GPU.