Worried about your graphics card overheating? GPU junction temperature might be the culprit.Understanding GPU Junction Temperature is key to keep your PC cool and your games smooth.
We’ll walk through what the junction temp is, why it matters, how to check it, and most importantly, when you should start worrying and what you can do about it. Stick with us – in just a few minutes, you’ll have the knowledge you need to keep your GPU running cool and boost its lifespan.
Whether you’re a first-time builder or a seasoned pro, you’ll pick up a few tips to keep things chill. Let’s dive in and master GPU junction temps!
What Is GPU Junction Temperature?
The GPU junction temperature refers to the highest temperature reading from your graphics card. It’s measured at the GPU die, which is the actual chip that does all the processing for graphics and video. This temperature reading gives you an idea of how hot your GPU is running and can help determine if it’s overheating.
An overheating GPU can cause damage to your graphics card over time and reduce its lifespan. High temperatures can also lead to thermal throttling, which means your GPU has to slow down to avoid overheating. This results in decreased performance in games and applications.
Also Read: What’s Average GPU Temp While Gaming? Comprehensive Guide
How to Check Your GPU Junction Temperature
The easiest way to monitor your junction temperature is through software like MSI Afterburner. This free tool provides an in-depth look at your graphics card’s temperature readings, clock speeds, fan speeds and more. Simply download and install Afterburner, open the app and you’ll see your current GPU junction temperature listed under the “Temperature” heading.
Other options include GPU-Z, HWMonitor and some graphics card manufacturer tools like EVGA Precision X1. These tools tap into temperature sensors on your specific graphics card to provide the junction temperature reading. They’re useful to keep open while gaming or doing other intensive tasks so you can check on your temps in real time and make any necessary adjustments.
Why GPU Junction Temperature Matters
GPUs are complex pieces of hardware that generate a lot of heat during intensive tasks like gaming or mining cryptocurrency. The GPU junction temperature refers to the hottest spot on the graphics card, usually directly under the GPU die. Keeping this temperature in check is important to prevent damage and ensure maximum performance.
When your GPU is working hard, the temperature can climb up to 95-105°C or higher. Anything over 100°C for extended periods of time can start to damage components and reduce the card’s lifespan. Thermal throttling may kick in, slowing down your GPU to prevent overheating and further damage. To avoid these issues, most graphics cards have built-in temperature sensors and fans to help regulate temperatures.
How to Monitor Your GPU Junction Temperature
To keep your graphics card healthy, you need to monitor its internal temperature. The GPU junction temperature refers to the hottest spot on your graphics card’s die. This temperature can often be 10-20°C higher than the overall GPU temperature, so it’s important to keep an eye on it.
Check Your GPU Software
The easiest way to view your GPU junction temp is through the software provided by your graphics card manufacturer. For NVIDIA cards, open the GeForce Experience app and click the “Performance” tab. This will show your GPU temperature, memory temperature, and junction temperature. AMD Radeon Software also provides temperature readings for your card.
Use a Third-Party Tool
If you prefer not to install extra software from NVIDIA or AMD, you can use a tool like GPU-Z, HWMonitor, or AIDA64. These free tools can provide a wealth of information about your graphics card, including current and maximum temperatures. Look for the reading labeled “GPU Junction” or “Hot Spot” to see your maximum GPU temp.
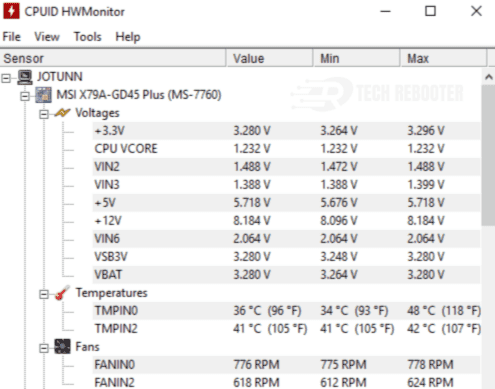
Aim For 90°C or Below
As a rule of thumb, you want your GPU junction temperature to stay below 90°C for optimal performance and stability. Anything above 95°C is in the danger zone and risks permanent damage to your graphics card. If your temps are running high, it’s a good idea to improve your case cooling by adding more fans or improving airflow. You can also undervolt your GPU to lower heat output, at the cost of a small performance decrease.
Also Read: How to Undervolt GPU for Better Performance?
Take Action If Overheating
If your GPU junction temperature spikes above 100°C, take immediate action to prevent damage. Shut down any intensive 3D tasks you’re running and give your graphics card time to cool. Consider improving your case cooling, reapplying thermal paste to your GPU, or even temporarily underclocking your graphics card until you can diagnose and fix the issue. Prolonged overheating can degrade components and reduce the lifespan of your graphics card.
Monitoring your GPU junction temperature regularly and making sure it stays in a safe range is one of the best ways to keep your graphics card running well for years to come. Pay attention to the readings from your GPU software and take action quickly if temperatures start to climb too high. Your graphics card will thank you!
Tips to Keep Your GPU Junction Temperature in Check
Your GPU (graphics processing unit) junction temperature refers to the hottest spot on your graphics card. Keeping this temperature in a safe range is important to prevent damage and ensure optimal performance. Here are some tips to help manage your GPU junction temperature:
Increase fan speed
The fans on your graphics card work to cool the components and lower the overall temperature. You can use a tool like MSI Afterburner to manually increase your fan speed. Start with increments of 5-10% at a time and check your temperature to find the optimal speed. The higher the fan speed, the more noise it will produce, so find a balance that keeps temperatures in check without becoming too loud.
Improve case airflow
Make sure you have good airflow in your PC case. This means intake fans at the front pulling in cool air, and exhaust fans at the back pushing out hot air. Remove any unused expansion slots or drive bays that could disrupt airflow. Keep your cables tied back and out of the way. The more freely the air can flow over and around your graphics card, the better.

Undervolt your GPU
Undervolting your graphics card can lower power consumption and decrease temperatures. Use a tool like MSI Afterburner to slightly lower the voltage to your GPU core and memory in small increments. Check for stability with a graphics stress test after each change. When instability occurs, raise the voltage slightly back up. Even a small undervolt can provide noticeable temperature improvements.
Repaste your GPU
Over time, the thermal paste between your graphics card’s GPU and the heatsink can dry out and lose effectiveness. Replacing the paste with a high-quality thermal compound can help significantly lower temperatures. The process requires removing the heatsink, cleaning off the old paste from the GPU and heatsink, and applying the new paste. Be very careful to avoid damaging any of the components. For most users, repasting a graphics card is an advanced process best left to a professional.

By following these tips, you should be able to better manage your GPU junction temperature and ensure the longest lifespan possible for your graphics card.
FAQs
What is GPU junction temperature?
- GPU junction temperature refers to the hottest spot on the graphics processing unit (GPU) chip itself. It’s often significantly higher than the temperature readings reported by software, which typically measure the GPU core or the surrounding area.
Why is GPU junction temperature important?
- Monitoring GPU junction temperature is crucial because excessive heat can lead to performance throttling, instability, and even permanent damage to the GPU.
What is a safe GPU junction temperature?
- Safe GPU junction temperatures can vary depending on the specific GPU model and manufacturer. However, a general guideline suggests staying below 85°C (185°F) for optimal performance and longevity. Some high-end GPUs may be rated for higher temperatures, but it’s always best to consult the manufacturer’s specifications.
How can I check my GPU junction temperature?
- Several software applications can monitor GPU temperatures, including GPU-Z, MSI Afterburner, and AMD Adrenalin software. These programs will often display both the GPU core temperature and the junction temperature.
How can I lower my GPU junction temperature?
- There are several ways to keep your GPU junction temperature under control:
- Ensure proper airflow within your computer case by cleaning dust from fans and vents.
- Consider upgrading your case fans for improved cooling.
- Adjust the GPU fan curve in your software for a more aggressive cooling profile (be mindful of noise levels).
- Undervolting your GPU can slightly reduce temperatures while maintaining performance (advanced users only).
- In extreme cases, consider replacing the thermal paste on your GPU (advanced users only).
Is there a difference between GPU temperature and VRAM temperature?
- Yes, GPU temperature refers to the graphics processing unit itself, while VRAM temperature refers to the video memory on the graphics card. Both are important to monitor, but VRAM typically runs cooler than the GPU junction.
Can overclocking increase GPU junction temperature?
- Yes, overclocking your GPU pushes it to work harder, which can significantly increase the junction temperature. Only overclock if you have proper cooling and are comfortable monitoring temperatures.
Is it normal for my GPU junction temperature to be higher than the core temperature?
- Yes, the GPU junction temperature is typically higher than the core temperature reported by software. This is because the junction is the hottest spot on the chip, while the core temperature represents an average across the entire chip.
Should I be worried if my GPU junction temperature reaches 90°C (194°F) or higher?
- While not ideal, occasional spikes up to 90°C (194°F) may be tolerable for short periods. However, consistently exceeding 90°C (194°F) can lead to throttling and potential damage. It’s best to take steps to improve cooling if your GPU runs this hot regularly.
Can a high GPU junction temperature damage my GPU?
- While occasional spikes above safe limits are unlikely to cause immediate damage, consistently high junction temperatures can degrade your GPU over time and shorten its lifespan. It’s important to monitor your temperatures and take action if they become excessive.
Conclusion
So there you have it. GPU junction temperature is an important metric to keep an eye on, but it doesn’t tell the whole story about your graphics card’s health. As long as you keep your GPU below 95C under load, you should be in good shape. Getting a beefier cooler can help lower temps, but don’t obsess over chasing the lowest number. Focus instead on overall system stability and performance. As long as your card isn’t throttling or causing crashes, a slightly higher junction temp is nothing to panic about. Take some time to monitor your temps and see what’s normal for your setup. A little knowledge goes a long way to helping you maximize the life of your GPU.