Are you wondering, does overclocking reduce GPU lifespan? Well, you’ve come to the right place. In this complete guide, we’ll walk through everything you need to know about overclocking your GPU. We’ll look at the effects it can have on lifespan and tips on how to overclock without damaging the computer.
What Is GPU Overclocking?
GPU overclocking is the process of increasing your graphics card’s clock speed to boost its performance. The “clock speed” refers to your GPU’s internal timer that synchronizes all the components. By increasing this clock speed, you can speed up your GPU and get better performance in games and applications.
How Does Overclocking Work?
Overclocking works by adjusting settings in your graphics card’s BIOS or through overclocking software. You can increase the clock speed of components like the core clock, memory clock, and shader clock. The core clock controls the main GPU processor, the memory clock handles the memory bandwidth, and the shader clock deals with graphics-rendering components.
Is Overclocking Safe?
When done properly, GPU overclocking is generally safe. However, it does come with risks like system instability, reduced component lifespan, and overheating. The key is to overclock in small increments, testing for stability with each change. Look for visual artifacts, system crashes, or other signs of instability. It’s also a good idea to monitor temperatures to make sure your graphics card does not overheat, which can cause permanent damage.
The Impact of Overclocking on GPU Lifespan
- Overclocking your graphics card can provide a nice performance boost for gaming and other graphics-intensive tasks. But running your GPU at higher clock speeds than intended by the manufacturer does come at a cost. Pushing your graphics card too hard for too long can negatively impact its lifespan.
- When you overclock a GPU, you’re forcing it to run at higher voltages and temperatures than normal. This additional stress reduces the lifespan of components like the graphics processor itself, memory modules, and the power delivery system. Typically, the higher the overclock and the longer it’s run, the more lifespan is reduced.
- For most casual overclocking, you’re looking at losing maybe a few months of usable life over the course of a couple years. But for extreme overclocking where you’re pushing the limits of stability, you could be shaving a year or more off the expected lifespan. The exact reduction is hard to quantify precisely, but as a rule of thumb, if you can keep your card under 80°C at full load when overclocked, the impact should be fairly minimal.
Tips to Overclock Your GPU Safely
To get more performance out of your graphics card, overclocking is a tempting option. However, overclocking also generates more heat and can reduce the lifespan of your GPU. The key is to overclock carefully and monitor your graphics card to avoid any permanent damage.
Increase Clock Speed in Small Amount
Don’t increase your GPU’s clock speeds all at once. Increase the core clock and memory clock in small amounts, like 10-20 MHz at a time. Boot into your PC and run a graphics benchmark or stress test after each increase to check for stability and temperature changes. If you see graphical glitches or your PC crashes, you’ve overclocked too far and should back down.
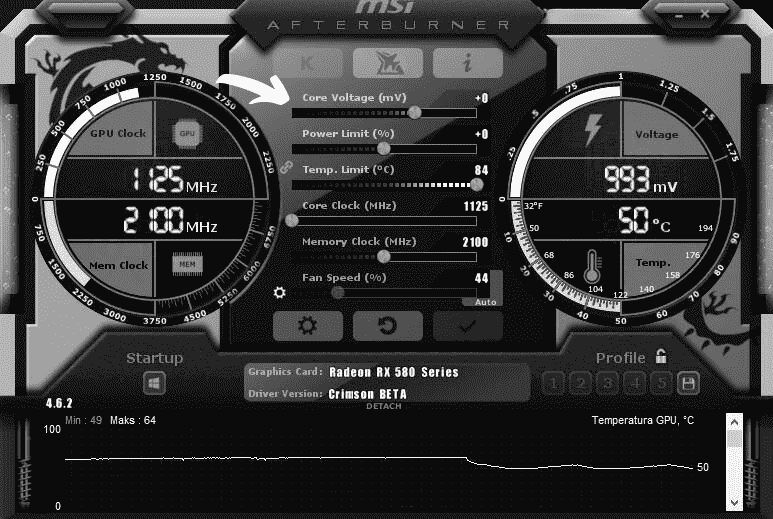
Monitor GPU Temperature
Overclocking generates extra heat, so monitor your GPU temperatures closely with an overclocking tool. Most graphics cards can handle temperatures up to 85°C, but lower is better. If temps climb above 80°C, you may need to improve your cooling or back down your overclock. Consider upgrading your case fans or installing an aftermarket CPU cooler to help exhaust more heat from your system.
Test for stability
Run benchmarks like 3DMark Fire Strike or the Unigine Heaven benchmark to test if your new overclock is stable under load. Look for graphical anomalies, texture flickering or other visual defects. Play a graphics-intensive game for at least 30 minutes to an hour. If you experience crashes, freezes or other issues, decrease your overclock settings.
Find the maximum safe overclock
Every graphics card overclocks differently based on its build quality and components. Slowly increase your clock speeds until you start seeing instability, then back down slightly. This is your card’s maximum safe overclock. Don’t exceed this overclock for daily use, as it could eventually cause permanent damage. Back down another 10% from this maximum for the best balance of performance and longevity.
With careful tuning and by avoiding aggressive overclocks, you can gain extra performance from your GPU without significantly impacting its lifespan. Monitor temperatures and test stability frequently, even after you find your maximum overclock. Be prepared to decrease settings if you notice issues down the road.
Optimal GPU Temperatures for Longevity
Your GPU generates a lot of heat when it’s working hard, like when you’re gaming or mining cryptocurrency. Higher temperatures over time can reduce the lifespan of your graphics card. As a rule of thumb, most GPUs can operate stably at up to 80-85°C, but lower temperatures are better for longevity.
Also Read: Idle GPU Temp: Is Your Card Too Hot?
Aim for 70°C or below under load
For the best longevity, aim to keep your GPU under 70°C when it’s working hard. At this temperature, degradation is minimal and your card should last for several years of heavy use. If your temps are in the 75-80°C range, your GPU will still work fine but its lifespan may be reduced by 6-12 months for every year of use.
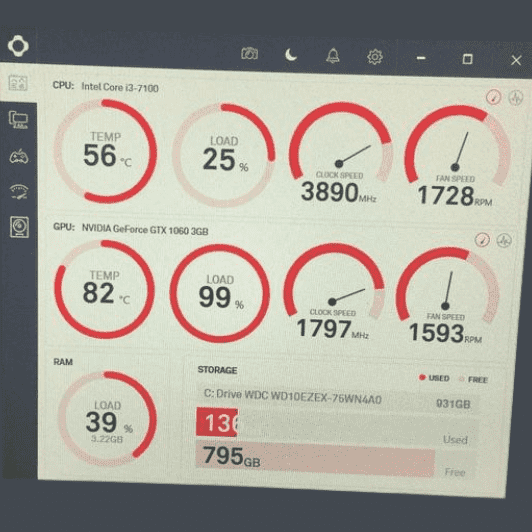
Improve cooling and airflow
There are a few ways to lower your GPU temperatures. First, make sure you have good airflow in your case. Add or upgrade case fans, and make sure there are no obstructions preventing air from flowing over and away from the GPU. You can also improve your GPU’s own cooling by replacing the thermal paste between the GPU die and heatsink, or upgrading to an aftermarket graphics card cooler.
Undervolt GPU
You may be able to lower temps by undervolting your GPU and optimizing settings. Undervolting reduces the power supplied to the GPU, which in turn reduces heat. Many GPUs can handle an undervolt of 10% or more without impacting performance. You can also turn down settings like power target, core clock, and memory clock. Lowering these settings will reduce performance, but can have a big impact on temperatures.
Also Read: How to Undervolt GPU for Better Performance?
Keeping temperatures in check will help maximize the lifespan of your graphics card. With regular monitoring and some simple tweaks to cooling and settings, you can keep your GPU running happily for years to come. Lower temps mean a longer life for your GPU, so taking steps to optimize cooling and reduce heat is well worth the effort.
FAQs
Does overclocking damage my GPU?
- Overclocking itself isn’t inherently damaging, but it increases heat and stress on your GPU. This can shorten its lifespan if not managed properly.
How much does overclocking reduce GPU lifespan?
- It’s difficult to say definitively. A moderate overclock with good cooling might only have a minimal impact. However, aggressive overclocking with high temperatures can significantly decrease lifespan.
What are the negatives of overclocking GPU?
- The negatives of overclocking a GPU include increased power consumption, higher temperatures leading to potential overheating, reduced component lifespan, voided warranties, instability leading to crashes or system damage, and incompatibility with certain applications or games.
Is a small performance gain worth the risk?
- That depends on your needs. If you’re a casual gamer, the performance boost might not be worth the potential risk. But for enthusiasts who want to squeeze every bit of power out of their GPU, the benefits might outweigh the drawbacks.
How can I overclock safely?
- Research your specific GPU to understand its overclocking potential. Start with small increments, prioritize good cooling, and monitor temperatures closely.
Are there alternatives to overclocking?
- Consider undervolting, which reduces power consumption and heat while offering a slight performance increase. Upgrading your cooling system can also improve performance without overclocking.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while overclocking can provide a performance boost, it also increases the strain on your GPU, potentially shortening its lifespan. It’s crucial to weigh the benefits against the risks and ensure proper cooling and monitoring to mitigate potential damage. Ultimately, responsible overclocking practices can extend the life of your GPU, but it’s essential to proceed with caution and prioritize longevity over immediate performance gains.