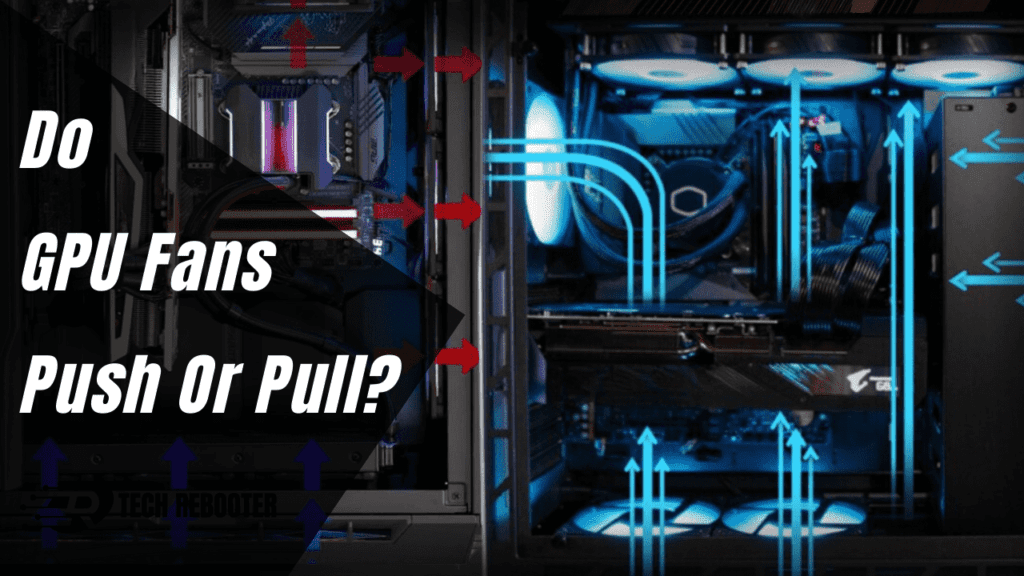
Are you looking to understand do gpu fans push or pull air? We get it, this GPU cooling stuff can be confusing. But don’t sweat it, we’ve got your back. Stick with us for the next few minutes and we’ll walk through exactly how the fans on your GPU work to keep things chill. By the end, you’ll be a pro at knowing whether those spinning blades are pushing air onto your card or pulling hot air away. Now let’s get to it!
GPU Cooling Basics: The Role of Fans
Your GPU (graphics processing unit) generates a lot of heat when it’s working hard, like when you’re gaming or doing other graphics-intensive tasks. To prevent overheating and keep your GPU running at peak performance, most GPUs rely on cooling fans. These fans can either push air onto the GPU to cool it or pull air away from the GPU.
Pushing Air Onto the GPU
Many GPUs use fans that intake air from inside your computer case and push it onto the surface of the GPU chip and surrounding components. As the air flows over the hot parts, it absorbs the heat before exiting the GPU enclosure. This method is very effective since the fans are directly cooling the GPU die and voltage regulation modules, which generate the most heat. The downside is that the hot air is exhausted into your case, which can raise the internal temperature over time.
Pulling Air Away from the GPU
Some higher-end GPUs use a blower-style fan that pulls air in from the GPU enclosure and exhausts it out the back of the case. This avoids dumping hot air into the case but may be slightly less efficient at directly cooling the GPU. However, the overall temperature inside the case will remain lower. Blower-style coolers often have to spin faster, so they can be noisier.
A Hybrid Approach
Many modern GPUs use a hybrid cooling approach with multiple fans. For example, two or three fans may intake and push air onto the GPU, while a blower-style fan exhausts some of the hot air from the enclosure. This provides the benefits of both methods by maximizing cooling and avoiding buildup of hot air in the case. The mix of fan types and directions also allows the fans to run at lower, quieter speeds overall.
Understanding GPU Fan: How it Works and Keeps Cool
GPU fans are designed to push hot air away from the graphics processing unit to prevent overheating. The fans spin at high speeds, pulling cooler air in and expelling warmer air out. This constant cycle of intake and exhaust is what keeps your GPU running at a stable temperature during intensive tasks like gaming or video editing.
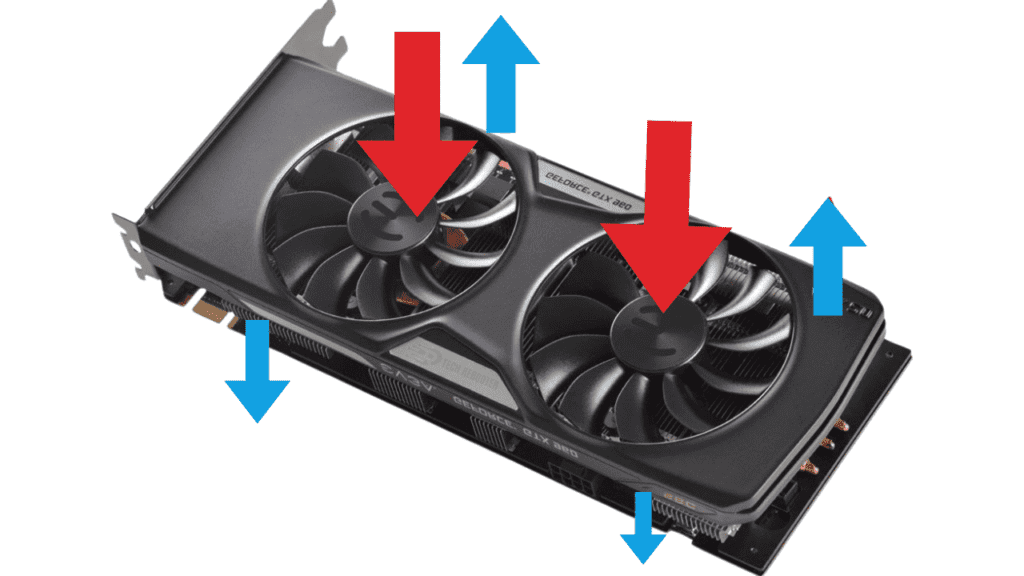
Cooling Fan Assembly
The typical GPU cooling fan assembly consists of two main components: an impeller and a shroud. The impeller, which contains the spinning blades, is attached to a motor that rotates at high RPMs. The shroud directs the flow of air over the impeller, maximizing its cooling efficiency. Some GPUs also have heatpipes that transfer heat from the GPU die to the fan assembly.
How the Air Flows
As the impeller spins, it pulls cooler air in through vents and intakes on your graphics card. The air flows over the GPU, absorbing heat as it goes. It is then pushed out of the card through exhaust vents and ports by the fast-spinning blades. This constant intake and exhaust of air keeps a steady flow of cooling circulation around your GPU.
Fan Speed Control
The speed of the cooling fans is dynamically controlled based on the GPU temperature. When idle or performing less intensive tasks, the fans spin slowly to minimize noise. During gaming or other GPU-heavy processes, the fans speed up to provide maximum cooling power. Most graphics cards allow you to create custom fan curves to customize cooling and acoustic performance.
Do GPU Fans Push or Pull Air?
Maintaining cool temperatures is crucial for optimal GPU performance. But how exactly do those tiny fans achieve this feat?
- The answer is pulling. Most GPUs utilize axial fans that pull air from the cooler environment within the case, directing it across the heatsink. This airflow absorbs heat from the GPU, and the now warmed air is exhausted out of the case, typically through the back or top of the graphics card.
This pulling action efficiently draws in fresh air and expels hot air, keeping your GPU running cool and preventing overheating.
Fan Configuration for Optimal Airflow
GPU cooling fans can either push or pull air to keep your graphics card at an optimal temperature. The configuration of the fans plays an important role in efficiently moving hot air away from the GPU.
Pushing Fans
- Fans that blow air onto the GPU are pushing the airflow, known as “pushing” fans. These fans, mounted on the graphics card, direct air flow onto the GPU chip and surrounding components.
Pulling Fans
- Graphics cards can also have fans that pull air away from the GPU, known as “pull” fans. These fans are mounted on the underside of the graphics card and draw hot air away from the components.
The optimal fan configuration for your GPU depends on its size and power. Powerful cards benefit from pull fans or push-pull setups, while moderate GPUs can use push fans. Check specs for recommended configuration to maintain performance and lifespan. Inadequate cooling can harm your GPU.
Providing good airflow and cooling for your GPU not only keeps it running at peak performance but also prevents long-term heat damage. Paying attention to factors like fan configuration, case cooling, and airflow can help keep your graphics card happy for years to come. Keeping an eye on your GPU temperature using a tool like MSI Afterburner is also a great way to make sure your cooling setup is working well.
Cooling Methods for GPUs
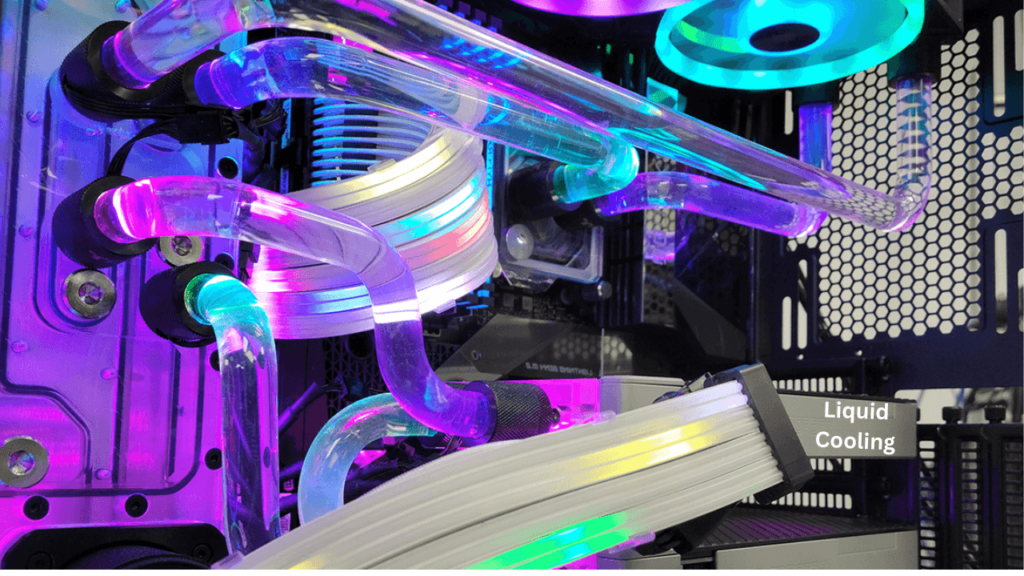
Liquid Cooling
Liquid cooling, where a liquid coolant circulates around the GPU to absorb and carry away heat, is an effective method for maximizing cooling. Closed-loop liquid coolers contain the coolant within the cooler unit, while open-loop systems circulate the coolant from an external reservoir. Liquid cooling can reduce GPU temperatures by up to 50°C compared to air cooling alone. However, liquid cooling systems tend to be more expensive, complex to install, and higher maintenance.

Thermal Paste
Thermal paste is a heat conductive compound you apply between the GPU chip and the graphics card’s heat sink to help transfer heat from the chip to the heat sink. Fresh, high-quality thermal paste can improve cooling by 5-10°C compared to old or low-quality paste.
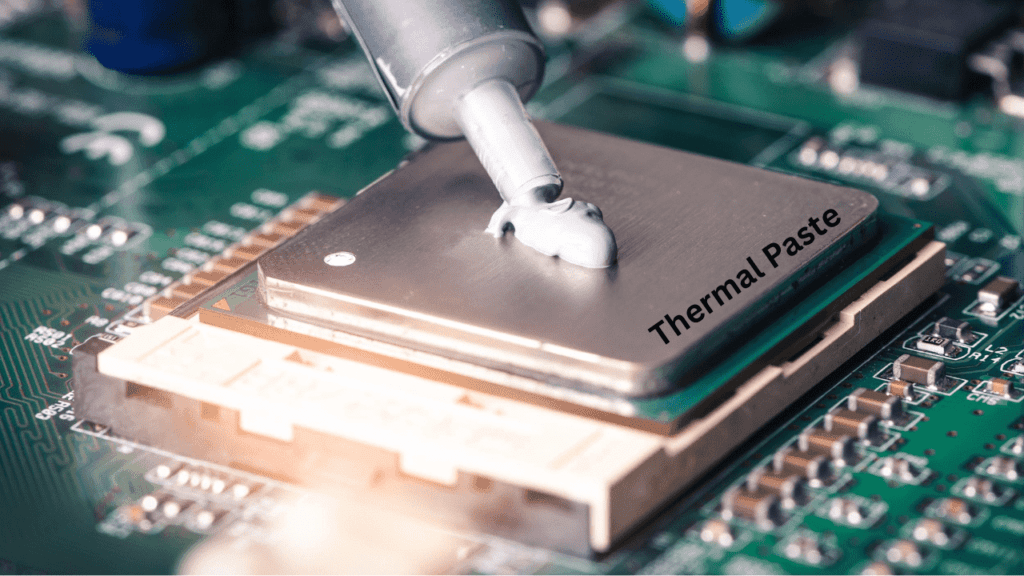
You’ll need to remove the existing thermal paste from your GPU chip and heat sink, then apply the new paste before reassembling your graphics card. Be very careful not to get thermal paste on any other components. Thermal paste is a good first step if you notice your GPU running hot before investing in more expensive cooling options.
Case Fan
Adding an additional case fan, especially one located near your graphics card, can improve airflow over and around your GPU to help carry more heat away. For the best results, use a high static pressure fan and consider setting it up as an intake fan blowing cool air directly onto your graphics card. An extra case fan probably won’t lower your GPU temperatures as much as the other methods here but can still provide a few degrees of improvement, and the fans are inexpensive and easy to install.
How Do I Know If My Fan is Push or Pull?
Figuring out if a fan is pushing or pulling air is crucial for optimal cooling, whether it’s in your computer, home, or car. Here are three quick methods:
Look for the Label
- Many fans have a sticker or label with an arrow indicating airflow direction. The pointed end of the arrow shows where the air is being pushed.
Observe the Blade Design
- If there’s no label, the fan blade shape can offer clues. The convex side (rounded outward) of the blades typically pulls air in, while the concave side (curving inward) pushes air out.
The “Tissue Test”
- If all else fails, grab a piece of tissue and hold it near the fan. The side that sucks the tissue in is the intake (pulling) side, and the opposite side is the exhaust (pushing) side.
By following these simple steps, you can quickly determine your fan’s airflow direction and ensure proper ventilation.
FAQs
Do all GPUs use the same type of fan?
- No, there are two main types of GPU fan configurations: push and pull. Push fans draw air in and force it over the heatsink, while pull fans draw air through the heatsink and exhaust it out the back of the card.
Which type of fan is better for my GPU?
- It depends on several factors, including your GPU’s power consumption and case airflow. Generally, more powerful GPUs benefit from pull fans or a combination of push and pull for better heat dissipation. Moderate GPUs often perform well with push fans.
How can I tell if my GPU fans are pushing or pulling air?
- The easiest way is to consult your GPU’s manual or specifications. Alternatively, you can try the “tissue test”: hold a tissue near the fan. If it gets sucked in, the fan is pulling air.
Can I change my GPU’s fan configuration?
- Modifying your GPU’s original configuration is not recommended as it can void your warranty and potentially damage your card. However, some advanced users might consider upgrading to a different cooler that uses a preferred fan configuration, but this should be done with caution and proper research.
What happens if my GPU doesn’t have good cooling?
- If your GPU doesn’t have adequate cooling, it can overheat, leading to performance throttling, crashes, and even permanent damage. Regularly monitoring your GPU’s temperature and ensuring proper airflow within your case are crucial for optimal performance and longevity.
Conclusion
Your GPU has fans that spin to push or pull air across the heatsink and keep things cool. Whether the fans push air into the GPU or pull air through depends on the specific design. But either way, they work to direct airflow and ventilate heat. Just keep those fans spinning clear of dust buildup so your graphics card stays chill. Now you know if your GPU fans push or pull air. Pretty simple when it comes down to it! You’re all set to keep your GPU running cool and fast.